
Back ليغنين Arabic لیقنین AZB Лігнін Byelorussian Лигнин Bulgarian Lignin BS Lignina Catalan Lignin Czech Lignin Danish Lignin German Λιγνίνη Greek
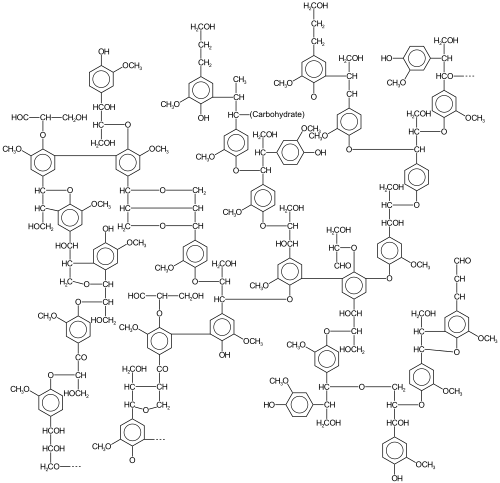
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants.[1] Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity and do not rot easily. Chemically, lignins are polymers made by cross-linking phenolic precursors.[2]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
UllLigwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Lebo, Stuart E. Jr.; Gargulak, Jerry D.; McNally, Timothy J. (2001). "Lignin". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. Kirk‑Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. doi:10.1002/0471238961.12090714120914.a01.pub2. ISBN 978-0-471-23896-6. Retrieved 2007-10-14.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search